DEVELOPMENT OF AN INJECTABLE SOLUTION OF ENROFLOXACIN 10 %
Keywords:
enrofloxacin; injectable; drug development; veterinaryAbstract
Enrofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone for veterinary use only, with broad-spectrum
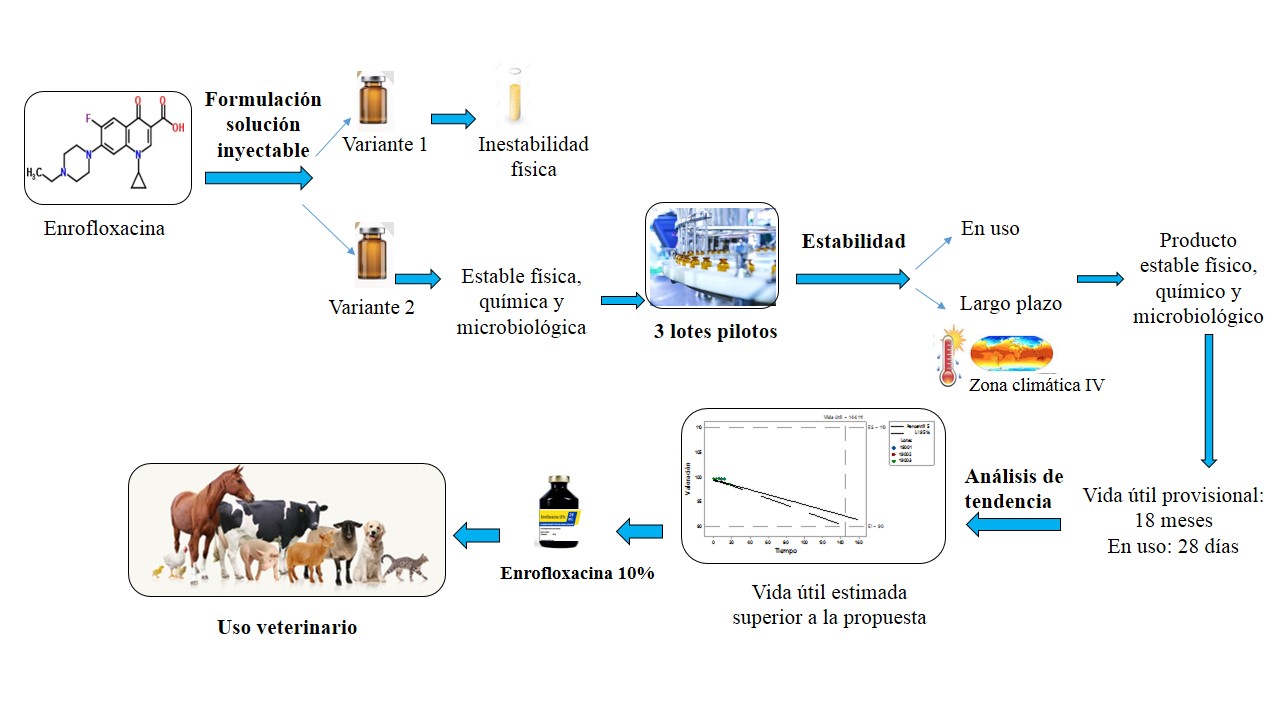
antimicrobial and mycoplasmicidal action. The objective of the work was to develop an
injectable solution of enrofloxacin 10 % for veterinary use. Two formulations were
prepared varying the use of solubilizer and cosolvents to achieve the solubility of the drug
and the one with the highest physical-chemical and microbiological stability was selected.
A long-term stability study was carried out on three pilot lots manufactured with the chosen
formulation for 18 months, as well as the stability in use of the product for 28 days.
Formulation variant two was selected for being the most stable. All batches met the quality
specifications established in the proposed storage conditions. The product is stable for 18
months and 28 days once the bottle is opened at room temperature and protected from light,
in 20 mL amber bulbs, so it can be used in veterinary medicine.
References
ORGANIZACIÓN INTERNACIONAL DE
SALUD ANIMAL. UNA SOLA SALUD. [;fecha de
consulta: 14-07-2023];. Disponible en:
https://www.woah.org/es/que-hacemos/iniciativasmundiales/una-sola-salud/
ORGANIZACIÓN MUNDIAL DE LA SALUD
(OMS). Ministerio de Salud Pública. República de
Cuba [;fecha de consulta: 14-07-2023];. Disponible
en: https://salud.msp.gob.cu/6-de-julio-dia-mundialde-las-zoonosis
ORGANIZACIÓN INTERNACIONAL DE
SALUD ANIMAL. El concepto una sola salud:
enfoque de la OIE 2021. Boletín No. 2013-1, pp. 1.
CANTERO, D.; BROWN, W.; GONZÁLEZ, M.;
FERNÁNDEZ, I.; VALDEZ, A. C. “Inocuidad
alimentaria versus residuos de medicamentos de uso
veterinario: un acercamiento a la panorámica actual”.
RCAN Rev Cubana Aliment Nutr 2021; 31 (1):236-
RNPS: 2221. ISSN: 1561-2929.
GONZÁLEZ, J.; MAGUIÑA, C.; GONZÁLEZ, F.
DE M. “La resistencia a los antibióticos: un problema
muy serio”. Acta Med Peru. 2019; 36 (2), 145-51.
ISSN 1728-5917. Disponible en:
http://www.scielo.org.pe/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext
&pid=S1728-59172019000200011
PLUMB, D. C. Plumb´s Veterinary Drug
Handbook. 7th ed. Stockholm Sweden: PharmaVet
Inc; 2011. ISBN: 978-0-470-95964-0.
SUMANO LÓPEZ, H. S. “Complejo recristalizado
de clorhidrato de enrofloxacina dihidratado, y método
para obtener el mismo”. [;Patente];, México,
WO2015088305A1, 2013. URL:
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2015088305A1/es
ŠANDOR, K. et al. “In-use stability of
enrofloxacin solution for injection in multi-dose
containers”. Acta Veterinaria (Beograd). 2012, 62 (2-
, 213-25.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2298/AVB1203213S
PATEL, K. M.; SUHAGIA, B. N.; SINGHVI, I.
“Analytical Method Development and Validation for
Enrofloxacin in Bulk and Formulation by RP-HPLC
Method”. American Journal of PharmTech Research.
, 8(2), 176-185. ISSN: 2249-3387. Disponible
en:
http://ajptr.com/assets/upload/publish_article/AJPTR82013_2658.pdf
YANG, F. et al. “Pharmacokinetics and tissue
distribution of enrofloxacin following single oral
administration in yellow river carp (Cyprinus carpio
haematoperus)”. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9. PMCID:
PMC 8855120. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2022.822032
FUENTES, V. O. “Resultados del estudio del
efecto interactivo entre amoxicilina y enrofloxacina
para uso en terapia y prevención de enfermedades en
medicina veterinaria”. Brazilian Journal of Animal and
Environmental Research, Curitiba. 2022, 5(2), 2228-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.34188/bjaerv5n2-065
ORGANIZACIÓN MUNDIAL DE SALUD
ANIMAL OIE. Lista de agentes antimicrobianos
importantes para la medicina veterinaria. Junio 2021.
[;fecha de consulta: 14-07-2023]; Disponible en:
https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2021/06/e-oielista-antimicrobianos-junio2021.pdf
HIMELFARB, M.; LANGRE, R.; MATÍAS, S.
“Evolución de los niveles séricos de enrofloxacina y
su metabolito activo, ciprofloxacina, tras
administración intramuscular y subcutánea en
llamas”. RCCV 2007; 1(2): 468-474. ISSN: 1988-
Disponible en:
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/38810036.pdf
DAUNDKAR, P. S.; VEMU, B.; DUMKA, V. K.;
SHARMA, S. K. “
Pharmacokinetic‐pharmacodynamic
integration of enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin
in buffalo calves”. Vet Med Sci. 2015; 1(2), 63-71.
Disponible en:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5645818/
MESQUITA, A. A.; MARCIO DA COSTA, G.
VIEIRA, F.; ALVES, F.; BRANDÃO, E. M. “Mastite
em rebanhos bubalinos e sua suscetibilidade a
antimicrobiano”. PUBVET 2017 Jan; 11(1): 62-73.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.22256/pubvet.v11n1.62-73
OTERO, J. L.; MESTORINO, N.; ERRECALDE,
J. O. “Enrofloxacina: una fluorquinolona de uso
exclusivo en veterinaria. Parte I: química, mecanismo
de acción, actividad antimicrobiana y resistencia
bacteriana”. Analecta veterinaria. 2001, 21(1), 31-41.
ISSN: 1514-2590. Disponible en:
https://core.ac.uk/reader/301032180
ASWATHY, S. R.; MUHAS, C.; ANJALI
SRUTHY, S.; DEVI SWAPNA, P. V.; GOPINATH,
U. “Validation and application of RP-HPLC method
for quantification of enrofloxacin in pure and
veterinary dosage forms”. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci.
; 14(2), 42-47. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22159/ijpps.2022v14i2.43053
XU, N. et al. “Plasma and tissue kinetics of
enrofloxacin and its metabolite, ciprofloxacin, in
yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) after a single
oral administration at different temperatures”. Journal
comparative biochemistry and physiology part c
toxicology and pharmacology. 2023; 266. 109554.
ISSN: 1532-0456. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2023.109554
International Council for Harmonisation of
Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for
Human Use. ICH Harmonised guideline. Validation
of analytical procedures Q2 (R2). Switzerland. ICH.
Disponible en:
https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/ICH_Q2-
R2_Document_Step2Guideline 2022 0324.pdf
CONTROL ESTATAL DE MEDICAMENTOS Y
DISPOSITIVOS MÉDICOS. Anexo 01 de la
Regulación No. 37-2012. Validación de métodos analíticos. La Habana. CECMED. 2014. Disponible en:
https://www.cecmed.cu/sites/default/files/adjuntos/Re
glamentacion/validaciondemetodosanaliticos.pdf
INSTITUTO DE MEDICINA VETERINARIA.
LABORATORIO DE CONTROL ESTATAL.
Requerimientos de los Estudios de Estabilidad para el
registro de medicamentos veterinarios nuevos y
conocidos. La Habana. IMV. 2003.
COMITÉ DE LAS AMÉRICAS DE
MEDICAMENTOS VETERINARIOS (CAMEVET).
Guía para la elaboración de estudios de estabilidad
de medicamentos veterinarios. Reg-Est 001.
CAMEVET. 2019. Disponible en: https://rramericas.woah.org/wp-content/uploads /2020 /03/regest-001-esp-por.pdf
TEMBHARE, E; RADHESHYAM, K.; JANRAO
M. “An approach to drug stability studies and shelflife determination”. Archives of Current Research
International. 2019, 19(1), 1-20. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.9734/ACRI/2019/v19i130147
ROMERO, M. “Estadística para estudios de
estabilidad (I)”. Pharmatech. 2019; 46, 38-40. ISSN:
-2105. Disponible en:
https://www.pharmatech.es/articulos/20191113/estadI
stica-para-estudios-estabilidad-1
Romero, M. “Estadística para estudios de
estabilidad (II)”. Pharmatech . 2020; 48, 32-33. ISSN:
-2105 Disponible en:
https://www.pharmatech.es/articulos/20200227/estadi
stica-estudios-estabilidad
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Lázara Sulin González-Ferre, Maybel Rosa González-Miraba, Yadira Aguado-Uribe, Rafael Francisco Semanat-Ferrer, Ylenia Piñero-Champagne

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content, based on the principle that offering the public free access to research helps a greater global exchange of knowledge. Each author is responsible for the content of each of their articles.






















