STRUCTURAL PHOSPHORUS AND IRON CO-DOPING OF NMC111 FOR LITHIUM ION BATTERIES
Keywords:
NMC111; Fe-P codoping; multifunctional materials; Li-ion batteriesAbstract
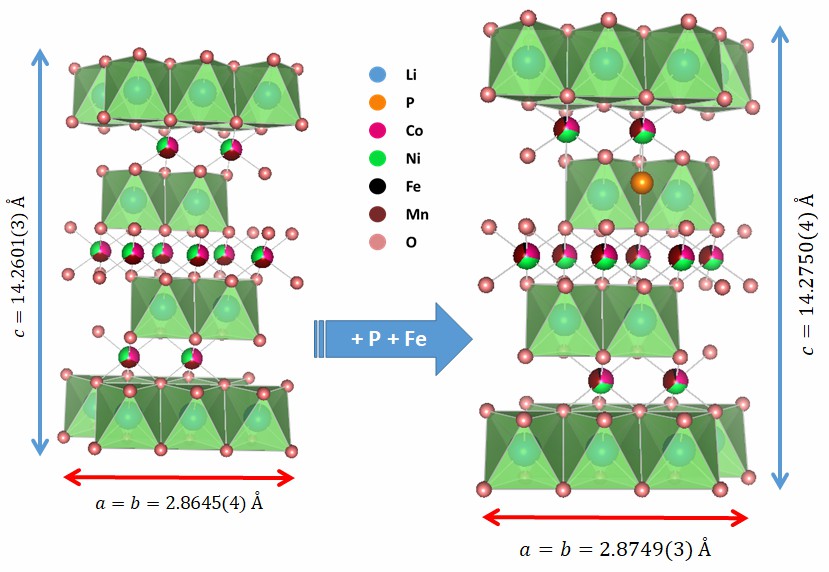
The family of cathode materials Li-NMC ( 0,33 ≤ x ≤ 0,85; 0,075 ≤ y ≤ 0,33) includes the most popular and widely used oxide in the field of lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, applying a proprietary and scalable synthesis method to transform it into a multifunctional material capable of functioning in Li cells induced by magnetic field and light represents a starting point in the goal of mastering these disruptive technologies. This work explores for the first time the codoping of Li-NMC111 oxide with iron (Fe3+) and phosphorus (P5+) and presents the results of characterization using structural, morphological, magnetic, and optical techniques. The results demonstrate the usefulness of the applied synthesis method to obtain NMC111 with the desired layered structure for its application in lithium-ion batteries, and that it can simultaneously host both dopants, which causes an increase in the dimensions of the unit cell, the particle size, the effective magnetic moment, and light absorption
References
HYUNG JOO, N. et al. "Comparison of the structural and electrochemical properties of layered Li [NixCoyMnz] O2 (x= 1/3; 0,5; 0,6; 0,7; 0,8 and 0,85) cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. (2013), 233, 121-130". Journal of Power Sources, 2013. 233: p. 121-130. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.01.063.
KRISHNA KUMAR, S. et al. "Synergistic effect of magnesium and fluorine doping on the electrochemical performance of lithium-manganese rich (LMR)-based Ni-Mn-Co-oxide (NMC) cathodes for lithium-ion batteries". Ionics. Springer, 2017. 23: p. 1655-1662. DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2018-9
LU, Y. et al. "Synthesis and characterization of Cu-doped LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 materials for Li-ion batteries". Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020. 844: p. 156-180. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156180
MALIK, M. et al. "Review on the synthesis of LiNixMnyCo1-x-yO2 (NMC) cathodes for lithium-ion batteries". Materials Today Energy, 2022. 28: 101066. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2022.101066
MI, C. et al. "Effect of iron doping on LiNi0.35Co0.30Mn0.35O2". Solid State Ionics, 2018. 325: p. 24-29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2018.07.022
WANG, C. et al. "Effects of Ca doping on the electrochemical properties of LiNi0. 8Co0. 2O2 cathode material". Solid State Ionics, 2006. 177(11-12): p. 1027-1031. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2006.03.030.
RODRÍGUEZ, R. A. et al. "The role of defects on the Jahn-teller effect and electrochemical charge storage in nanometric LiMn2O4 material". Solid State Ionics, 2021. 369: p.115707. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2021.115707
RODRÍGUEZ, R. A. et al. "Impact of phosphorus structural position on the electrochemical enhancement of phosphorus doped LiMn2O4". Electrochimica Acta, 2020. 337: 135712. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.135712
RODRÍGUEZ, R. A. et al. "Compounds. P and Fe doping, a strategy to develop light and magnetic responsive multifunctional materials: The case of LiMn2O4". Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024. 978: 172837. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.172837
LEYVA NAVARRO, E. et al. "Caracterización y evaluación de propiedades físico-químicas y eléctricas del hidróxido de níquel (II), obtenido con licores industriales". Rev. Cubana Química, 2023. 35(2): p.215-237. Available from: https://cubanaquimica.uo.edu.cu/index.php/cq/article/download/5332/4742
ARABOLLA RODRÍGUEZ, R. et al. "Manganese spinels co-doped with iron and phosphorus for photo- or magnetic field-assisted li-ion cells and their preparation method". WO/2024/208381, PCT/CU2024/050001, Universidad de La Habana [;CU];/[;CU];, 11/03/2024. Available from: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/WO2024208381
LE BAIL, A. et al. "Whole powder pattern decomposition methods and applications: A retrospection". Powder-diffraction, 2005. 20(4): p. 316-326. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1154/1.2135315
NITHYA, C. et al. "Synthesis of high voltage (4.9 V) cycling LiNi x Co y Mn 1− x− y O 2 cathode materials for lithium rechargeable batteries". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2011. 13(13): p. 6125-6132. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CP02258F
DENG, C. et al. "Effect of synthesis condition on the structure and electrochemical properties of Li [;Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3]; O2 prepared by hydroxide co-precipitation method". Electrochimica Acta , 2008. 53(5): p. 2441-2447. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.10.025
SUN, H. et al. "Electronic structure and comparative properties of LiNi x Mn y Co z O2 cathode materials". The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017. 121(11): p. 6002-6010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b00810
JULIEN, C. et al. "Local cationic environment in lithium nickel-cobalt oxides used as cathode materials for lithium batteries". Solid State Ionics , 2000. 136: p. 887-896. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(00)00503-8
ROUGIER, A. et al. "Vibrational spectroscopy and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.7Co0.3O2 cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries". Ionics, 1997. 3: 170-176. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375613
NAKAMOTO, K. Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds, part B: applications in coordination, organometallic, and bioinorganic chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. 2009. ISBN: 0470405872, 978047040587. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470405888
AIT SALAH, A. et al. "FTIR features of lithium iron phosphates used as positive electrodes in rechargeable lithium batteries". Electrochemical Society Proceedings, 2005. 14: p. 103-112. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1149/MA2005-01/35/1385
GARCÍA, J. C. et al. "Strain-driven surface reconstruction and cation segregation in layered Li (Ni 1− x− y Mn x Co y) O 2 (NMC) cathode materials". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2020. 22(42): p. 24490-24497. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP03942J
GARCÍA, J. C. et al. "Surface structure, morphology, and stability of Li (Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3)O2 cathode material". The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017. 121(15): p. 8290-8299. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b00896
PING, M. et al. "Revealing magnetic ground state of a layered cathode material by muon spin relaxation and neutron scattering experiments". Appl. Phys. Lett., 2019. 114: p. 203901. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5096620
XIN, X. G. et al. "Structural and magnetic properties of LiNi0. 5Mn1. 5O4 and LiNi0. 5Mn1. 5O4− δ spinels: A first-principles study". Chinese Physics B, 2012. 21(12): p. 128-202. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/21/12/128202
ABDELAZIZ CADI, E. et al. "DFT+U Study of the Electronic, Magnetic and Mechanical Properties of Co, CoO, and Co3O4". Journals Sabinet, 2023. 74: p. 8-16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17159/0379-4350/2021/v74a3
TORRENT, J. et al. "Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy". Science Society of America, 2008. 5: p. 367-385. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.5.c13
WEST, A. R. Solid state chemistry and its applications: John Wiley & Sons. 2022. ISBN: 978-1-119-94294-8. Available from: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Solid+State+Chemistry+and+its+Applications%2C+2nd+Edition-p-9781118447444
TORRENT, J. et al. "Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy of iron oxides". Encyclopedia of surface and Colloid Science, 2002. ISBN-13. 978-1466590458 ; Edition. 3rd ; Publisher. CRC Press 1: p. 1438-1446.
LEE, A. et al. "Photo-accelerated fast charging of lithium-ion batteries". Nature communications, 2019. 10(1): p. 4946. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12863-6
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Roberto Domínguez-Rodríguez, Adrián Enríquez-Martínez, Manuel Ávila-Santos, Yodalgis Mosqueda-Laffita, Eduardo L. Pérez-Cappe

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content, based on the principle that offering the public free access to research helps a greater global exchange of knowledge. Each author is responsible for the content of each of their articles.






















