CO-DOPAJE ESTRUCTURAL DEL NMC111 CON HIERRO Y FÓSFORO PARA BATERÍAS DE ION LITIO
Palavras-chave:
NMC111; codopaje Fe-P; materiales multifuncionales; baterías de ion-LiResumo
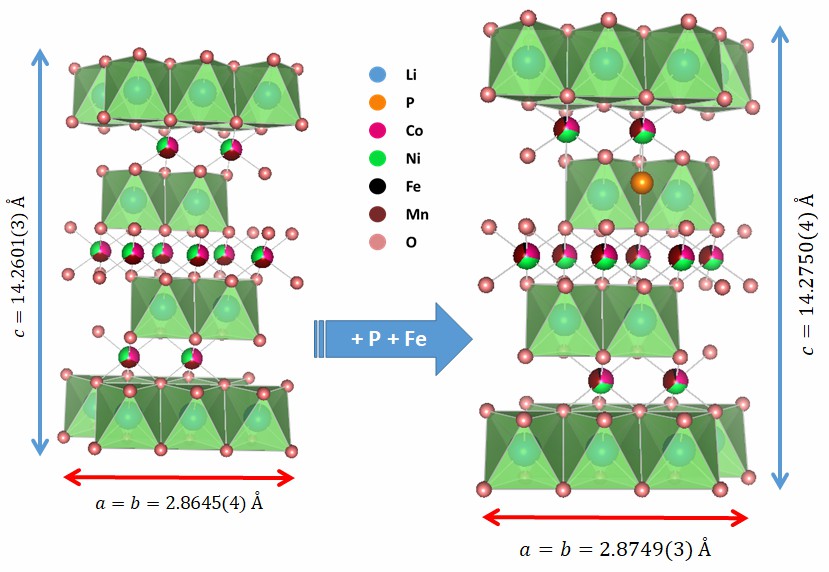
La familia de materiales catódicos Li-NMC ( 0,33 ≤ x ≤ 0,85; 0,075 ≤ y ≤ 0,33) comprende los óxidos más utilizados en el campo de las baterías de ion litio. Por ello, aplicar un método de síntesis propio y escalable, para transformarlo en un material multifuncional con capacidad para desempeñarse en celdas de Li bajo campo magnético o luz, constituye un punto de partida en el propósito de dominar estas tecnologías disruptivas. En este trabajo se explora, por primera vez, el codopaje del óxido Li-NMC111 con hierro (Fe3+) y fósforo (P5+), y se presentan los resultados de la caracterización por técnicas estructurales, morfológicas, magnéticas y ópticas. Los resultados demuestran la utilidad del método de síntesis, aplicado para obtener el Li-NMC111 codopado con la estructura laminar deseada para su aplicación en baterías de ion-Li, y el aumento de las dimensiones de la celda unitaria, del tamaño de las partículas, del momento magnético efectivo y de la absorción luminosa
Referências
HYUNG JOO, N. et al. "Comparison of the structural and electrochemical properties of layered Li [NixCoyMnz] O2 (x= 1/3; 0,5; 0,6; 0,7; 0,8 and 0,85) cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. (2013), 233, 121-130". Journal of Power Sources, 2013. 233: p. 121-130. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.01.063.
KRISHNA KUMAR, S. et al. "Synergistic effect of magnesium and fluorine doping on the electrochemical performance of lithium-manganese rich (LMR)-based Ni-Mn-Co-oxide (NMC) cathodes for lithium-ion batteries". Ionics. Springer, 2017. 23: p. 1655-1662. DOI https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2018-9
LU, Y. et al. "Synthesis and characterization of Cu-doped LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 materials for Li-ion batteries". Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020. 844: p. 156-180. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156180
MALIK, M. et al. "Review on the synthesis of LiNixMnyCo1-x-yO2 (NMC) cathodes for lithium-ion batteries". Materials Today Energy, 2022. 28: 101066. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2022.101066
MI, C. et al. "Effect of iron doping on LiNi0.35Co0.30Mn0.35O2". Solid State Ionics, 2018. 325: p. 24-29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2018.07.022
WANG, C. et al. "Effects of Ca doping on the electrochemical properties of LiNi0. 8Co0. 2O2 cathode material". Solid State Ionics, 2006. 177(11-12): p. 1027-1031. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2006.03.030.
RODRÍGUEZ, R. A. et al. "The role of defects on the Jahn-teller effect and electrochemical charge storage in nanometric LiMn2O4 material". Solid State Ionics, 2021. 369: p.115707. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssi.2021.115707
RODRÍGUEZ, R. A. et al. "Impact of phosphorus structural position on the electrochemical enhancement of phosphorus doped LiMn2O4". Electrochimica Acta, 2020. 337: 135712. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.135712
RODRÍGUEZ, R. A. et al. "Compounds. P and Fe doping, a strategy to develop light and magnetic responsive multifunctional materials: The case of LiMn2O4". Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2024. 978: 172837. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.172837
LEYVA NAVARRO, E. et al. "Caracterización y evaluación de propiedades físico-químicas y eléctricas del hidróxido de níquel (II), obtenido con licores industriales". Rev. Cubana Química, 2023. 35(2): p.215-237. Available from: https://cubanaquimica.uo.edu.cu/index.php/cq/article/download/5332/4742
ARABOLLA RODRÍGUEZ, R. et al. "Manganese spinels co-doped with iron and phosphorus for photo- or magnetic field-assisted li-ion cells and their preparation method". WO/2024/208381, PCT/CU2024/050001, Universidad de La Habana [;CU];/[;CU];, 11/03/2024. Available from: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/WO2024208381
LE BAIL, A. et al. "Whole powder pattern decomposition methods and applications: A retrospection". Powder-diffraction, 2005. 20(4): p. 316-326. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1154/1.2135315
NITHYA, C. et al. "Synthesis of high voltage (4.9 V) cycling LiNi x Co y Mn 1− x− y O 2 cathode materials for lithium rechargeable batteries". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2011. 13(13): p. 6125-6132. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CP02258F
DENG, C. et al. "Effect of synthesis condition on the structure and electrochemical properties of Li [;Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3]; O2 prepared by hydroxide co-precipitation method". Electrochimica Acta , 2008. 53(5): p. 2441-2447. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2007.10.025
SUN, H. et al. "Electronic structure and comparative properties of LiNi x Mn y Co z O2 cathode materials". The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017. 121(11): p. 6002-6010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b00810
JULIEN, C. et al. "Local cationic environment in lithium nickel-cobalt oxides used as cathode materials for lithium batteries". Solid State Ionics , 2000. 136: p. 887-896. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(00)00503-8
ROUGIER, A. et al. "Vibrational spectroscopy and electrochemical properties of LiNi0.7Co0.3O2 cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries". Ionics, 1997. 3: 170-176. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02375613
NAKAMOTO, K. Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds, part B: applications in coordination, organometallic, and bioinorganic chemistry. John Wiley & Sons. 2009. ISBN: 0470405872, 978047040587. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470405888
AIT SALAH, A. et al. "FTIR features of lithium iron phosphates used as positive electrodes in rechargeable lithium batteries". Electrochemical Society Proceedings, 2005. 14: p. 103-112. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1149/MA2005-01/35/1385
GARCÍA, J. C. et al. "Strain-driven surface reconstruction and cation segregation in layered Li (Ni 1− x− y Mn x Co y) O 2 (NMC) cathode materials". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2020. 22(42): p. 24490-24497. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP03942J
GARCÍA, J. C. et al. "Surface structure, morphology, and stability of Li (Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3)O2 cathode material". The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2017. 121(15): p. 8290-8299. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b00896
PING, M. et al. "Revealing magnetic ground state of a layered cathode material by muon spin relaxation and neutron scattering experiments". Appl. Phys. Lett., 2019. 114: p. 203901. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5096620
XIN, X. G. et al. "Structural and magnetic properties of LiNi0. 5Mn1. 5O4 and LiNi0. 5Mn1. 5O4− δ spinels: A first-principles study". Chinese Physics B, 2012. 21(12): p. 128-202. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/21/12/128202
ABDELAZIZ CADI, E. et al. "DFT+U Study of the Electronic, Magnetic and Mechanical Properties of Co, CoO, and Co3O4". Journals Sabinet, 2023. 74: p. 8-16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17159/0379-4350/2021/v74a3
TORRENT, J. et al. "Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy". Science Society of America, 2008. 5: p. 367-385. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2136/sssabookser5.5.c13
WEST, A. R. Solid state chemistry and its applications: John Wiley & Sons. 2022. ISBN: 978-1-119-94294-8. Available from: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Solid+State+Chemistry+and+its+Applications%2C+2nd+Edition-p-9781118447444
TORRENT, J. et al. "Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy of iron oxides". Encyclopedia of surface and Colloid Science, 2002. ISBN-13. 978-1466590458 ; Edition. 3rd ; Publisher. CRC Press 1: p. 1438-1446.
LEE, A. et al. "Photo-accelerated fast charging of lithium-ion batteries". Nature communications, 2019. 10(1): p. 4946. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12863-6
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2025 Roberto Domínguez-Rodríguez, Adrián Enríquez-Martínez, Manuel Ávila-Santos, Yodalgis Mosqueda-Laffita, Eduardo L. Pérez-Cappe

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Esta revista oferece acesso aberto imediato ao seu conteúdo, com base no princípio de que oferecer ao público o acesso gratuito à pesquisa contribui para uma maior troca global de conhecimento.






















