BENEFITS OF ACID ACTIVATION TO OBTAIN ACTIVATED CARBONS FROM SUGARCANE BAGASSE
Keywords:
bagazo de caña, carbón; activación ácida; caracterización.Abstract
Translator
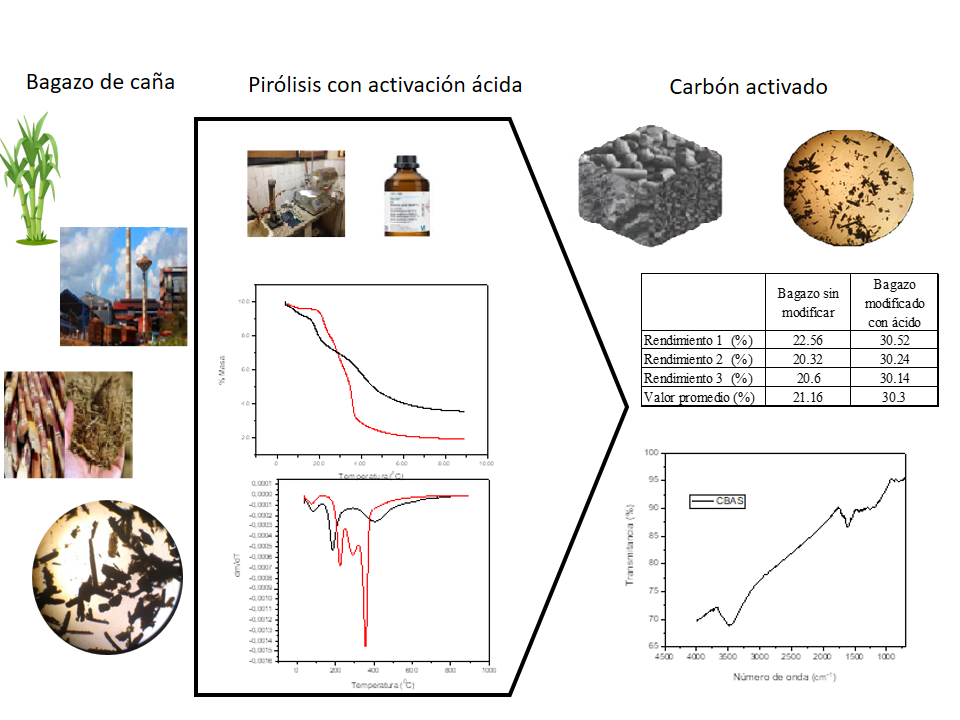
The objective of this research is to obtain porous coals from sugar cane bagasse, using acid activation, as well as its characterization, which includes the kinetics of its pyrolysis. For this purpose, solid analysis techniques were used, such as: immediate and elemental analysis, thermal analysis (thermogravimetry, derived thermogravimetry and differential scanning calorimetry), optical microscopy and infrared spectroscopy with fourier transform. Through immediate and elemental analysis, it is evident that sugarcane bagasse can be used as a carbon source. The thermolysis shows the influence of the chemical activator and through the kinetic study it is identified that the kinetic models D3 and F1 determine the reaction rate for the stages involved. The FTIR spectra and the optical microscopy image demonstrate the greater extent of the reaction and beneficit of the acid activation.
References
- DEMIRBAS, A. “Combustion systems for biomass
fuel”. Energy Sources, Part A. 2007, 29 (4), 303-312.
doi: http://doi.org/10.1080/009083190948667
- ALBIS, A. y col. “Pirólisis de hemicelulosa
catalizada por sulfato de zinc y sulfato férrico”. Rev.
Ion. 2018; 31(2), 37-49. doi:
http://doi.org/10.18273/revion.v31n2-2018003
- SEBASTIÁN NOGUÉS, F.; GARCÍA GALINDO,
D.; REZEAU, A. Energía de la biomasa. Volumen 1,
Prensas Universitarias de Zaragoza, España, 2010.
ISBN: 978-84-92774-91-3.
- MCKENDRY, P. “Energy production from
biomass (part 1): overview of biomass”. Bioresource
technology, 2002, 83 (1), 37-46. doi:
http://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-8524(01)00118-3
- PENEDO MEDINA, M; SÁNCHEZ DEL CAMPO
LAFITA, A; FALCÓN HERNÁNDEZ, J. “Pirólisis
de bagazo de caña a escala de laboratorio. Parte I:
Influencia de condiciones de operación en el
rendimiento de productos”. Tecnología Química.
, XXVIII (2), pp. 61-70. ISSN: 0041-8420.
- ADINAVEEN, T.; JUDITH VIJAYA, J.; JOHN
KENNEDY, L. “Comparative study of electrical
conductivity on activated carbons prepared from
various cellulose materials”. Arab J Sci Eng, 2014,
, 55-65. doi: http://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-
-6
- AMIN M., T.; ALAZBA A., A.; SHAFIQ, M.
“Removal of Copper and Lead using Banana Biochar
in Batch Adsorption Systems: Isotherms and Kinetic
Studies”. Arab J Sci Eng , 2017, 43, 5711-5722. doi:
http://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-017-2934-z
- AO, Y.; XUA, J.; FUA, D.; YUANA, CH. “A
simple route for the preparation of anatase titaniacoated magnetic porous carbons with enhanced
photocatalytic activity”. Carbon, 2008, 46, 596-603.
doi: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2008.01.009
- HU, Y.; CHEN, X.; LIU, Z.; WANG, G.; LIAO, S.
“Activated carbon doped with biogenic manganese
oxides for the removal of indigo carmine”. Journal of
Environmental Management, 2016, 166, 512e518.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.10.043
- YAKOUT, S. M., SHARAF EL DEEN,G.
“Characterization of activated carbon prepared by
phosphoric acid activation of olive stones”. Arabian
Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 9, S1155-S1162.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2011.12.002
- CASTRO, J. B.; BONELLI, P. R.; CERRELLA,
E. G.; CUKIERMAN, A. L. “Phosphoric acid
activation of agricultural residues and bagasse from
sugar cane: influence of the experimental conditions
on adsorption characteristics of activated carbons”.
Ind. Eng Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 4166-4172. doi:
http://doi.org/10.1021/ie0002677
- TZONG HORNG, LIOU. “Development of
mesoporous structure and high adsorption capacity of
biomass-based activated carbon by phosphoric acid
and zinc chloride activation”. Chemical Engineering
Journal, 2010, 158, 129-142. doi:
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.12.016
- UNE-EN-14774-1. “Biocombustibles sólidos.
Procedimiento para el secado de biomasas”. Norma
española, septiembre 2010.
- BAHÍN DERONCELÉ, L. J.; QUESADA
GONZÁLEZ, O.; CASCARET CARMENATY, D.
A.; ODIO GONZÁLEZ, R. A.; CANTOS-MACÍAS,
M. A. “Obtención de material carbonoso de bagazo de
caña de azúcar con activación salina”. Rev. Cubana
Quím, 2020, 35 (2), 253-273. e-ISSN: 2224-5421.
- UNE-EN- 15148. “Biocombustibles sólidos.
Determinación del contenido de materia volátil”.
Norma española, septiembre 2010.
- UNE-EN-14775. “Biocombustibles sólidos.
Método para la determinación del contenido de
cenizas”. Norma española, septiembre 2010.
- PARIKH, J.; CHANNIWALA, S. A.; GHOSAL,
G. K. “A correlation for calculating elemental
composition from proximate analysis of biomass
materials”. Fuel, 2007, 86(12), 1710-1719.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.06.028
- ALMANSA CARRASCOSA, M. C. Preparación
de discos de carbón activado químicamente para
almacenamiento de metano, 2021. Tesis de doctorado.
Universidad de Alicante. España. URL:
http://hdl.handle.net/10045/9102
- DAMARTZIS, Th. et al. “Thermal degradation
studies and kinetic modeling of cardoon
(Cynaracardunculus) pyrolysis using
thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)”. Bioresource
technology , 2011, 102(10), 6230-6238.
https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00009-2
- CARDOSO, C. R.; MIRANDA, M. R.; SANTOS,
K. G.; ATAÍDE, C. H. “Determination of kinetic
parameters and analytical pyrolysis of tobacco waste
and sorghum bagasse”. Journal of Analytical and
Applied Pyrolysis, 2011, 92, 392-400. doi:
http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2011.07.013
- Feng Xu et al. “Qualitative and quantitative
analysis of lignocellulosic biomass using infrared
techniques: A mini-review”. Applied Energy, 2013,
, 801-809.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dannis A. Cascaret-Carmenaty, Roilan A. Odio-González, Manuel Á. Cantos-Macías, Maylen Caballero-Fuentes, Omaida Quesada-González

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content, based on the principle that offering the public free access to research helps a greater global exchange of knowledge. Each author is responsible for the content of each of their articles.






















