REMOVAL AQUEOUS ARSENIC SPECIES USING ELEMENTAL IRON AND ITS SPECIATION/DETECTION BY HPLC-ICPMS
Keywords:
arsenic speciation; iron nanoparticles; iron microparticles; pollutionAbstract
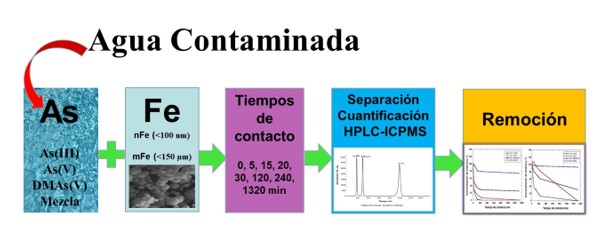
The use of elemental iron (nano and microparticles) for the removal of aqueous arsenic
species and its speciation by HPLC-ICPMS, was evaluated. The nanoparticles were
obtained by reacting of ferric chloride with sodium borohydride and, the microparticles
were commercial iron powder. The experiments were carried out for As(III), DMAs(V) and
As(V), individually and in mixture, at different times and were analyzed by HPLC-ICPMS.
The results show, that both forms of elemental iron, contribute the decrease in the initial
concentration of As(III) and As(V) by increasing the contact time, obtaining greater
changes in the presence of nanoparticles (99,9 %, 240 min) with adsorption capacity
(< 499,5 µg/g). For DMAs(V) there were not significant changes in its initial concentration.
This demonstrates the feasibility of elemental iron to remove some aqueous arsenic
species and, that the values depend on the chemical composition of arsenic, it may be
viable for inorganic species.
References
BHAT, A.; O´HARA, T.; TIAN, F.; SINGH, B.
"Review of analytical techniques for arsenic detection
and determination in drinking water". Environmental
Science: Advances, 2023, 2: 171-195. Doi:
http://doi.org/10.1039/d2va00218c
WHO. (2018). Arsénico. Consultado el 01/11/2022.
Disponible en: https://www.who.int/es/newsroom/fact-sheets/detail/arsenic.
CESEÑA QUIÑONEZ, J. I.; RAMOS RAMÍREZ,
E.; SERAFÍN MUÑOZ, A. H.; MORENO
PALMERIN, J.; ZANOR, G. A.; GUTIÉRREZ
ORTEGA, N. L. "Remoción de arsénico del agua para
consumo humano empleando un hidróxido doble
laminar Mg/Fe". Acta Universitaria, 2019, 29, 1-12.
Doi. http://dx.doi.org/10.15174/au.2019.2499
REID, M. S. et al. "Arsenic speciation analysis: A
review with an emphasis on chromatographic
separations". Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2020,
, 115770, 1-14. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.115770
NICOMEL, N. R.; LEUS, K.; FOLENS, K.; VAN
DER VOORT, P.; DU LAING, G. "Technologies for
arsenic removal from water: current status and future
perspectives". Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health,
, 13(1), 62. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13010062
BALARAM, V.; COPIA, L.; SARAVANA
KUMAR, U.; MILLER, J.; CHIDAMBARAM, S.
"Pollution of water resources and application of ICPMS techniques for monitoring and management-A
comprehensive review". Geosystems and
Geoenvironment, 2023, 2(4), 100210. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geogeo.2023.100210
EL GUIATY, M. A.; EL KADI, A. O. S. "The
duality of arsenic metabolism: impact on human
health". Annual Review of Pharmacology and
Toxicology, 2023, 63, 341-358. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-051921-
HABUDA STANIC, M.; NUJIC, M. "Arsenic
removal by nanoparticles: a review". Environ Sci
Pollut Res, 2015, 22, 8094-8123. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4307-z
KATSOYIANNIS, I. A.; ZOUBOULIS, A. I.;
MARTIN, J. "Kinetics of Bacterial As(III) Oxidation
and Subsequent As(V) Removal by Sorption onto
Biogenic Manganese Oxides during Groundwater
Treatment"
. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2004, 43(2), 486-
Doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/ie030525a
BEDNAR, A. J.; GARBARINO, J. R.;
BURKHARDT, M. R.; RANVILLE J. F.;
WILDEMAN, T. R. "Field and laboratory arsenic
speciation methods and their application to naturalwater analysis". Water Research, 2004, 38(2):355-
Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.09.034
VILTRES, H.; ODIO, O. F.; BORJA, R.;
AGUILERA, Y.; REGUERA, E. “Magentite
nanoparticle for arsenic remotion” Journal of Physics:
Conf. Series, 2017, 792, 012078. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/792/1/012078
LIU, P.; LIANG, Q.; LUO, H.; FANG, W.;
GENG, J. "Synthesis of nano-scale zero-valent
iron-reduced graphene oxide-silica nanocomposites for the efficient removal of arsenic
from aqueous solutions". Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2019, 26(32), 33507-33516. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06320-6
TERLECKA, E. "Arsenic speciation analysis in
water samples: a review of the hyphenated
techniques". Environ Monit Assess, 2005, 107, 259-
Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-3109-z
CASTILLEJOS, A.; GATTI, L.M.; KERL, C. F.,
CHENNU, A.; KLATT, J. M. "Arsenic speciation
analysis in porewater by a novel colorimetric assay",
Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 827,
Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154155
KELLER, N. S.; STEFÁNSSON, A.;
SIGFÚSSON, B. "Determination of arsenic speciation
in sulfidic waters by Ion Chromatography HydrideGeneration Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (ICHG-AFS)". Talanta, 2014, 128, 466-472. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.04.035
JEONG, S.; LEE, H.; KIM, Y.; YOON, H.
"Development of a simultaneous analytical method to
determine arsenic speciation using HPLC-ICP-MS:
Arsenate, arsenite, monomethylarsonic acid,
dimethylarsinic acid, dimethyldithioarsinic acid, and
dimethylmonothioarsinic acid". Microchemical
Journal, 2017, 134, 295-300, Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2017.06.011
MONGA, Y. et al. "Sustainable synthesis of
nanoscale zerovalent iron particles for environmental
remediation". Chem Sus Chem, 2020, 13(13), 3288-
Doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202000290
MONDAL, P.; MAJUMDER, C. B.; MOHANTY,
B. “Laboratory based approaches for arsenic
remediation from contaminated water: Recent
developments”. Journal of Hazardous Materials B,
, 137(1), 464-479. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.023
ZHANG, W. "Nanoscale iron particles for
environmental remediation: An overview". Journal of
Nanoparticle Research, 2003, 5, 323-332.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1025520116015
VILAS, J. L. "Nanotecnología como herramienta
para la recuperación de suelos". Consultado el 31 oct
Disponible. https://docplayer.es/30742148-
Jose-luis-vilas-vilela-departamento-de-quimica-fisicalaboratorio-de-quimica-macromolecular-upv-ehu.html
SIMEONOVA V.; RIVERA, M.; PIÑA, M.;
AVÍLES, M.; CASTREJÓN, S. "Evaluación de diversos
minerales para la remoción de arsénico de agua para
consumo humano". 1997. Consultado el 07/11/2022.
Disponible en:
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Evaluaci%C3%
B3n-de-diversos-minerales-para-la-remoci%C3%B3nSimeonovaHuerta/c1a37c7677c9252a5c3f3661819d6d75e8717c72
BARRIENTOS, J. E.; MATUTES A. J. "Uso de
nanomateriales para la remoción de arsénico del agua
para consumo humano". Mundo Nano, 2013, 6(11).
Doi:
https://doi.org/10.22201/ceiich.24485691e.2013.11
BANG S.; KORFIATIS, G. P.; MENG, X.
“Removal of arsenic from water by zero-valent iron”.
J Hazard Mater, 2005, 121(1-3), 61-67. Doi:
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 María Maldonado-Santoyo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
This journal provides immediate open access to its content, based on the principle that offering the public free access to research helps a greater global exchange of knowledge. Each author is responsible for the content of each of their articles.






















