REMOCIÓN DE ESPECIES ACUOSAS DE ARSÉNICO USANDO HIERRO ELEMENTAL Y SU ESPECIACIÓN/DETECCIÓN POR HPLC-ICPMS
Palavras-chave:
especiación de arsénico; nanopartículas y micropartículas de hierro; contaminaciónResumo
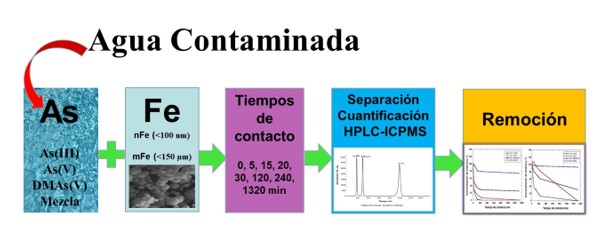
Se evaluó el uso de hierro elemental (nano y micropartículas) para la remoción de especies
acuosas de arsénico y su especiación por HPLC-ICPMS. Las nanopartículas se obtuvieron
por reacción de cloruro férrico con borohidruro de sodio, y las micropartículas fueron
hierro en polvo comercial. Los experimentos se realizaron para As(III), DMAs(V) y As(V),
individualmente y en mezcla a diferentes tiempos, y se analizaron por HPLC-ICPMS. Los
resultados muestran, que ambas formas de hierro elemental, favorecen la disminución en la
concentración inicial de As(III) y As(V) al aumentar el tiempo de contacto, obteniéndose
mayores cambios en presencia de las nanopartículas (99,9 %, 240 min) con capacidad de
adsorción > 499,5 µg/g. Para el DMAs(V) no hubo cambios significativos en su
concentración inicial. Esto demuestra la factibilidad del hierro elemental para remover
algunas especies de arsénico en disolución, y que los valores dependen de la composición
química del arsénico, pudiendo ser viable para las especies inorgánicas.
Referências
BHAT, A.; O´HARA, T.; TIAN, F.; SINGH, B.
"Review of analytical techniques for arsenic detection
and determination in drinking water". Environmental
Science: Advances, 2023, 2: 171-195. Doi:
http://doi.org/10.1039/d2va00218c
WHO. (2018). Arsénico. Consultado el 01/11/2022.
Disponible en: https://www.who.int/es/newsroom/fact-sheets/detail/arsenic.
CESEÑA QUIÑONEZ, J. I.; RAMOS RAMÍREZ,
E.; SERAFÍN MUÑOZ, A. H.; MORENO
PALMERIN, J.; ZANOR, G. A.; GUTIÉRREZ
ORTEGA, N. L. "Remoción de arsénico del agua para
consumo humano empleando un hidróxido doble
laminar Mg/Fe". Acta Universitaria, 2019, 29, 1-12.
Doi. http://dx.doi.org/10.15174/au.2019.2499
REID, M. S. et al. "Arsenic speciation analysis: A
review with an emphasis on chromatographic
separations". Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2020,
, 115770, 1-14. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.115770
NICOMEL, N. R.; LEUS, K.; FOLENS, K.; VAN
DER VOORT, P.; DU LAING, G. "Technologies for
arsenic removal from water: current status and future
perspectives". Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health,
, 13(1), 62. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13010062
BALARAM, V.; COPIA, L.; SARAVANA
KUMAR, U.; MILLER, J.; CHIDAMBARAM, S.
"Pollution of water resources and application of ICPMS techniques for monitoring and management-A
comprehensive review". Geosystems and
Geoenvironment, 2023, 2(4), 100210. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geogeo.2023.100210
EL GUIATY, M. A.; EL KADI, A. O. S. "The
duality of arsenic metabolism: impact on human
health". Annual Review of Pharmacology and
Toxicology, 2023, 63, 341-358. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-051921-
HABUDA STANIC, M.; NUJIC, M. "Arsenic
removal by nanoparticles: a review". Environ Sci
Pollut Res, 2015, 22, 8094-8123. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4307-z
KATSOYIANNIS, I. A.; ZOUBOULIS, A. I.;
MARTIN, J. "Kinetics of Bacterial As(III) Oxidation
and Subsequent As(V) Removal by Sorption onto
Biogenic Manganese Oxides during Groundwater
Treatment"
. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2004, 43(2), 486-
Doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/ie030525a
BEDNAR, A. J.; GARBARINO, J. R.;
BURKHARDT, M. R.; RANVILLE J. F.;
WILDEMAN, T. R. "Field and laboratory arsenic
speciation methods and their application to naturalwater analysis". Water Research, 2004, 38(2):355-
Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.09.034
VILTRES, H.; ODIO, O. F.; BORJA, R.;
AGUILERA, Y.; REGUERA, E. “Magentite
nanoparticle for arsenic remotion” Journal of Physics:
Conf. Series, 2017, 792, 012078. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/792/1/012078
LIU, P.; LIANG, Q.; LUO, H.; FANG, W.;
GENG, J. "Synthesis of nano-scale zero-valent
iron-reduced graphene oxide-silica nanocomposites for the efficient removal of arsenic
from aqueous solutions". Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2019, 26(32), 33507-33516. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06320-6
TERLECKA, E. "Arsenic speciation analysis in
water samples: a review of the hyphenated
techniques". Environ Monit Assess, 2005, 107, 259-
Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-3109-z
CASTILLEJOS, A.; GATTI, L.M.; KERL, C. F.,
CHENNU, A.; KLATT, J. M. "Arsenic speciation
analysis in porewater by a novel colorimetric assay",
Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 827,
Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154155
KELLER, N. S.; STEFÁNSSON, A.;
SIGFÚSSON, B. "Determination of arsenic speciation
in sulfidic waters by Ion Chromatography HydrideGeneration Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry (ICHG-AFS)". Talanta, 2014, 128, 466-472. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.04.035
JEONG, S.; LEE, H.; KIM, Y.; YOON, H.
"Development of a simultaneous analytical method to
determine arsenic speciation using HPLC-ICP-MS:
Arsenate, arsenite, monomethylarsonic acid,
dimethylarsinic acid, dimethyldithioarsinic acid, and
dimethylmonothioarsinic acid". Microchemical
Journal, 2017, 134, 295-300, Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2017.06.011
MONGA, Y. et al. "Sustainable synthesis of
nanoscale zerovalent iron particles for environmental
remediation". Chem Sus Chem, 2020, 13(13), 3288-
Doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202000290
MONDAL, P.; MAJUMDER, C. B.; MOHANTY,
B. “Laboratory based approaches for arsenic
remediation from contaminated water: Recent
developments”. Journal of Hazardous Materials B,
, 137(1), 464-479. Doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.023
ZHANG, W. "Nanoscale iron particles for
environmental remediation: An overview". Journal of
Nanoparticle Research, 2003, 5, 323-332.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:1025520116015
VILAS, J. L. "Nanotecnología como herramienta
para la recuperación de suelos". Consultado el 31 oct
Disponible. https://docplayer.es/30742148-
Jose-luis-vilas-vilela-departamento-de-quimica-fisicalaboratorio-de-quimica-macromolecular-upv-ehu.html
SIMEONOVA V.; RIVERA, M.; PIÑA, M.;
AVÍLES, M.; CASTREJÓN, S. "Evaluación de diversos
minerales para la remoción de arsénico de agua para
consumo humano". 1997. Consultado el 07/11/2022.
Disponible en:
https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Evaluaci%C3%
B3n-de-diversos-minerales-para-la-remoci%C3%B3nSimeonovaHuerta/c1a37c7677c9252a5c3f3661819d6d75e8717c72
BARRIENTOS, J. E.; MATUTES A. J. "Uso de
nanomateriales para la remoción de arsénico del agua
para consumo humano". Mundo Nano, 2013, 6(11).
Doi:
https://doi.org/10.22201/ceiich.24485691e.2013.11
BANG S.; KORFIATIS, G. P.; MENG, X.
“Removal of arsenic from water by zero-valent iron”.
J Hazard Mater, 2005, 121(1-3), 61-67. Doi:
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2025 María Maldonado-Santoyo

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Esta revista oferece acesso aberto imediato ao seu conteúdo, com base no princípio de que oferecer ao público o acesso gratuito à pesquisa contribui para uma maior troca global de conhecimento.






















