Obtención, caracterización y aplicaciones de materiales nanoestructurados para el desarrollo fenológico del cultivo de la lechuga
Palabras clave:
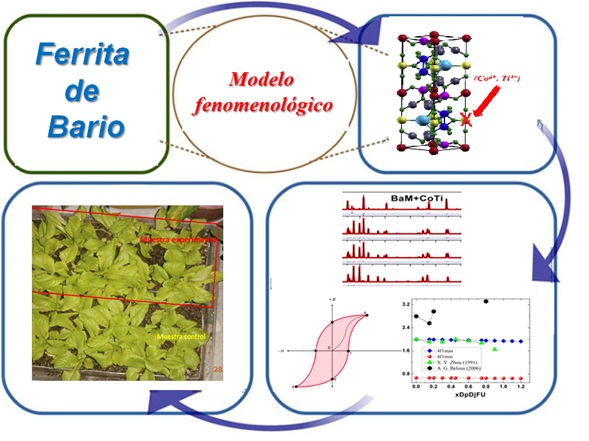
modelo fenomenológico; materiales nanoestructurados; hexaferritas tipo-M; lechugasResumen
En esta investigación, se aplican expresiones semiempíricas, para el cálculo de los principales parámetros
cinéticos de obtención de fases del tipo: BaFe12-2x (Dp2+, Dj4+)x
O19 (BaM+(Dp2+, Dj4+)x
). Fue actualizada
la última variante de un modelo fenomenológico, de distribución de cationes en los diferentes sitios de la
estructura cristalográfica, para la predicción de algunas propiedades físicas, antes y después de ser dopadas
las muestras. La interpretación física de las caracterizaciones estructurales, micro-estructurales, y magnéticas
de las fases obtenidas, fue realizada. La interpretación física de las caracterizaciones físico-químicas
realizadas, da lugar al diseño potencial de aplicaciones de estos compuestos, como imanes permanentes. En
esta propuesta se da como ejemplo de aplicación a escala de laboratorio, la utilización de uno de estos imanes
de BaFe12-2x (Co2+, Ti4+)xO19 (BaM+(Co2+,Ti4+)x) para el estudio cualitativo, de todo el desarrollo fenológico
de plantas de lechugas, en un campo magnético permanente.
Citas
YUJIE YANG et al. “Preparation of Al3+-Co2+ co-substituted M-type SrCaNd hexaferrites and their controlled magnetic properties”; Aip Advances 8, 075212 (2018). https://doi.org/10. 1063/1.5034451
LIM, J. P.; KANG, M. G.; KANG, Y. M. “Development of Multi-Cation-Doped M-Type Hexaferrite Permanent Magnets”; Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 295-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ app13010295
ZHANG, W. et al. “Structure, Spectra, Morphology, and Magnetic Properties of Nb5+ Ion-Substituted Sr Hexaferrites”. Magneto Chemistry, 2022, 8, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry8050051
YOU, J. Y.; LEE, K. H.; KANG, Y. M.; YOO, S. I. “Enhancement of the Magnetic Properties in Si4+-Li+-Substituted M-Type Hexaferrites for Permanent Magnets”. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12 12295. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122312295
VIVEK DIXIT et al. “Site preference and magnetic properties of Zn-Sn-substituted strontium hexaferrite”. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 173901. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5084762
VIVEK DIXIT et al. “Site preference and magnetic properties of Ga/In-substituted strontium hexaferrite: An ab initio study”. J. Appl. Phys. 118, 203908 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4936368
P. A MARIÑO CASTELLANOS; A. C. MORENO BORGES; G. OROZCO MELGAR; J. A. GARCÍA; E. GOVEA ALCAIDE. “Structural and magnetic study of the Ti4+-doped barium hexaferrite ceramic samples: Theoretical and experimental results”. Physica B: Condensed Matter (2011), 406, 3130–3136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2011.03.084
P. A. MARIÑO CASTELLANOS et al. “Predictions and Magnetic Characterization of M-type Hexaferrites Doped with Two Cations in the Fe3+ Site”. American Journal of Engineering and Technology Management.2019, 4 (6): 83-90. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajetm.20190406.12
MOHAMMAD SARRAF et al. “Magnetic Field (MF) Applications in Plants: An Overview”. Plants 2020, 9, 1139-1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091139; www.mdoi.com/journal/plants
NEO E. NYAKANE; E. D. MARKUS; M. M. SEDIBE. “The Effects of Magnetic Fields on Plants Growth: A Comprehensive Review”, International Journal of Food Engineering, 2019, 5(1): 79-87, https://doi.org/10.18178/ijfe.5.1.79-87
SUNG YONG AN; IN-BO SHIM; CHUL SUNG KIM. “Mössbauer and magnetic properties of Co–Ti substituted barium hexaferrite nanoparticles”. Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 91, 8465-8475; https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1452203
X. Z. ZHOU,; A. H. MORRISH; Z. W. LI; Y. K. HONG. “Site preference for Co2+ AND Ti4+ in CO-Ti substituted barium ferrite”. Ieee transactions on magnetics, 1991, 27:6 4654-4656. https://doi.org/10.1109/20.27890
A. G. BELOUS; O. I. V’YUNOV; E. V. PASHKOVA; V. P. IVANITSKII; O. N. GAVRILENKO. “Mössbauer Study and Magnetic Properties of M-Type Barium Hexaferrite Doped with Co+Ti and Bi+Ti Ions”. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 26477-26481. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp064628t
ARAFAT ABDEL HAMED ABDEL LATEF; MONA F. A. Dawood; Halimeh Hassanpour; Maryam Rezayian; Nabil A. Younes. “Impact of the Static Magnetic Field on Growth, Pigments, Osmolytes, Nitric Oxide, Hydrogen Sulfide Phenylalanine Ammonia-Lyase Activity, Antioxidant Defense System, and Yield in Lettuce”. Biology 2020, 9, 172, 1-19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9070172
ACUÑA, R.; NAGUELQUIN, F.; GARCÍA, F.; TORRES, J. “Application of magnetic fields (CM) and their relationship with recovery viability and vigor in aged seeds of Lactuca sativa L. Agro Sur 47(1):2019, 9-21. https://doi.org/10.4206/agrosur:2019.v47n1-04
ARAÚJO, S. et al. “Physical Methods for Seed Invigoration: Advantages and Challenges in Seed Technology”. Front. Plant Sci. (2016) 7:646, 1-12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00646
PAUL GALLAND; ALEXANDER PAZUR. “Magnetoreception in plants”. J. Plant Res. (2005) 118:371-389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-005-0246-y
MROCZEK ZDYRSKA, M.; TRYNIECKI, Ł.; KORNARZYŃSKI, K.; PIETRUSZEWSKI, S.; GAGOŚ, M. “Influence of magnetic field stimulation on the growth and biochemical parameters in Phaseolus vulgaris l”. Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology & Food Sciences, 2016, 5(6): p548-551.https://doi.org/10.15414/jmbfs.2016.5.6.548-551
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 Pedro Antonio Mariño-Castellanos, Eduardo Fernández-Santiesteban, Arles Vega-García, Yadir Hidaldo-Peña, Nuris Ludmila Castellanos-Hall

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Esta revista proporciona un acceso abierto inmediato a su contenido, basado en el principio de que ofrecer al público un acceso libre a las investigaciones ayuda a un mayor intercambio global de conocimiento. Cada autor es responsable del contenido de cada uno de sus artículos.






















